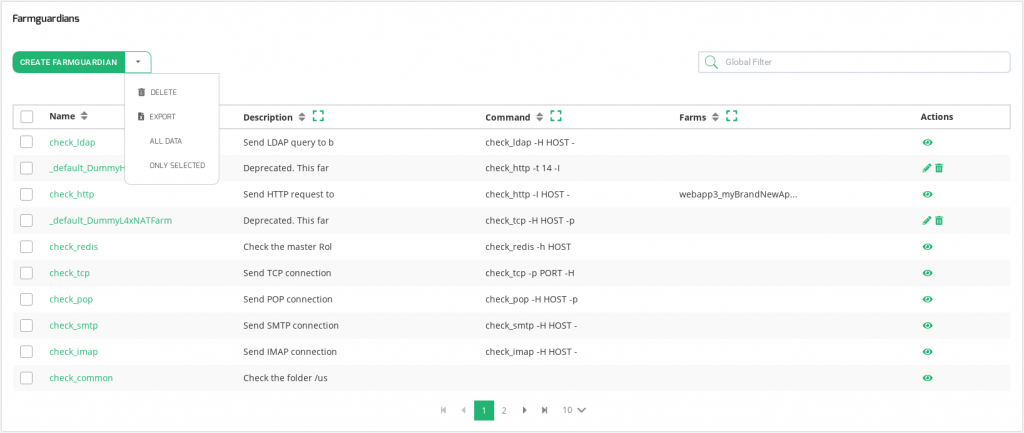
The Farmguardian section lists all the available health checks in the load balancer, a short description of each one and the farms where they’re applied.
Farmguardian is used for advanced monitoring state of backends. When a problem is detected by Farmguardian it automatically disables the real server and will be marked as blacklisted.
Health checks could be both pre-configured or custom. The two types of checks can be identified through the action column, the checks with the eye icon are pre-configured and the checks with the pencil and trash icon are custom checks.
Through the Action menu the following actions are available:
- Create Farmguardian. Open the Farmguardian creation form.
- Delete. To destroy the selected Farmguardian check.
The information in the Farmguardian table includes:
Name. Descriptive name of the Farmguardian check.
Description. This field can contain some description of a certain health check.
Command. Check command and parameters to be executed on every interval against each backend of the farm.
Farms. Farms and services that use a certain check.
Actions. Allowed actions are:
- Edit. It opens the configure screen of the Farmguardian check. Only available for custom farmguardian checks.
- Delete. Delete that Farmguardian check. If the check is assigned on any service, then a notification will ask you if force the delete. Only for custom farmguardian checks.
- Show. It shows the global settings which are not editable. Only for pre-configured farmguardian checks.
The columns: description, command, and farms are limited to 20/30 characters, if it appears ellipsis, you can press over expand icon of that column ![]() to see the complete list. After you can press over the collapse icon of that column
to see the complete list. After you can press over the collapse icon of that column ![]() to delimited the column again.
to delimited the column again.
Pre-configured health checks
The available built-in health checks that could be used for your farms are the following:
check_tcp: Tries to open a TCP connection to backend.
check_http: Send HTTP request to backend and expect a 200 OK response with a timeout of 5 secs.
check_https: Send HTTPS request to backend and expect a 200 OK response with a timeout of 5 secs.
check_http_response_string: Send HTTP request to backend, expect a 200 OK response and a given string in the HTML with a timeout of 5 secs. Change string by value to find in the response.
check_https_response_string: Send HTTP request to backend and expect a response of 200 OK and a given string in the HTML with a timeout of 5 secs. Change string by value to find in the response.
check_ldap: Send LDAP query to backend and expect LDAP bind with a timeout of 5 secs. Change -b (base search), -D (user to bind), -P (user password).
check_ldaps: Send LDAPS query to backend and expect LDAP bind with a timeout of 5 secs. Change -b (base search), -D (user to bind), -P (user password).
check_smtp: Send SMTP connection to backend and expect an SMTP response OK with a timeout of 5 secs.
check_imap: Send IMAP connection to backend and expect an IMAP response OK with a timeout of 5 secs.
check_pop: Send POP connection to backend and expect a POP response OK with a timeout of 5 secs.
check_udp: Send UDP connection to backend and check if the port is opened.
check_ping: Send 2 ICMP packets and check that the 100% reaches the host.
check_common: Check the folder /usr/local/zevenet/libexec, which includes more checks, get more info about the health check through the command line with
Next step, create a custom Farmguardian check.