By default, Zevenet runs simple health checks to the backends or real servers, but sometimes this check is not enough to determine if backends are working properly. For this reason, Zevenet implements a service that executes and manages advanced health checks via a daemon that uses plugins called Farmguardian.
The main task of Farmguardian is to work as an advanced monitoring tool for applications’ backends, for this purpose, Farm Guardian reads the farm configuration and obtains the backend list, and helped by a plugin checks the backend health status, Farm Guardian updates the backend status for the given farm managing if the load balancer should send traffic to such backend.
In this section, you can configure the Farmguardian check. You can see two tabs Global and Farms.
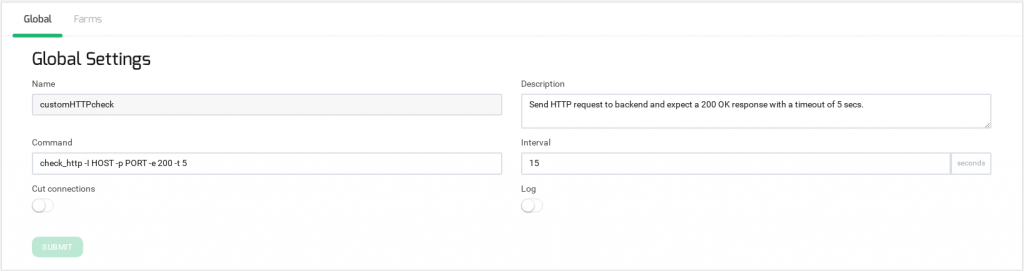
Global Settings
On the Global section, there are health checks settings for certain Farmguardian health check, as it’s shown below.
The fields of this tab are not editable if the check is pre-loaded in the system, if you want to modify that check, you should Create a new Farmguardian enabling the copy param and adding the desired check as a template and modify the new.
- Name. Identification name of the current Farm Guardian check, it can not be edited.
- Description. This field contains a brief description of the Farmguardian check.
- Command. Set the command executed in order to check backends status.
- Interval. Time in seconds between health check batches against all the backends. Notice that each interval time, the farmguardian check will stop and be relaunched, so it must be high enough to be able to check all backends ( timeout * nº backends +1 )
- Cut Connections. When this option is enabled, the current connections of the detected down backend are flushed, forcing an immediate reconnection to an available backend. If disabled, the current connections will be drained without disconnecting any client.
- Logs. Enables or disables the logs of every farmguardian check. With logs disabled only the backend status changes are shown in the log files.
Configure health checks
All available Farmguardian plugins can be found under the directory /usr/local/zevenet/app/libexec/ inside of the load balancer.
Farm Guardian uses plugins in order to configure advanced health checks to detect if a certain real server is working as expected using customized options. There are a lot of health checks for every kind of protocol, service or application. The most important plugins are described below.
check_ftp: This plugin tests FTP connections with the specified host.
Usage: check_ftp -H host -p port [-w <warning time>] [-c <critical time>] [-s <send string>] [-e <expect string>] [-q <quit string>][-m <maximum bytes>] [-d <delay>] [-t <timeout seconds>] [-r <refuse state>] [-M <mismatch state>] [-v] [-4|-6] [-j] [-D <warn days cert expire>[,<crit days cert expire>]] [-S <use SSL>] [-E]
check_fping: This plugin will use the fping command to ping the specified host for a fast check.
Usage: check_fping <host_address> -w limit -c limit [-b size] [-n number] [-T number] [-i number]
check_http: This plugin tests the HTTP service on the specified host. It can test plain (HTTP) and secure (HTTPS) protocols, follow redirects, it searches for strings and regular expressions, check connection times, and report on certificate expiration times, HTTP return codes, etc.
Usage:
check_http -H <vhost> | -I <IP-address> [-u <uri>] [-p <port>]
[-J <client certificate file>] [-K <private key>]
[-w <warn time>] [-c <critical time>] [-t <timeout>] [-L] [-E] [-a auth]
[-b proxy_auth] [-f <ok|warning|critcal|follow|sticky|stickyport>]
[-e <expect>] [-d string] [-s string] [-l] [-r <regex> | -R <case-insensitive regex>]
[-P string] [-m <min_pg_size>:<max_pg_size>] [-4|-6] [-N] [-M <age>]
[-A string] [-k string] [-S <version>] [--sni] [-C <warn_age>[,<crit_age>]]
[-T <content-type>] [-j method]
check_imap: This plugin tests IMAP connections with the specified host.
Usage: check_imap -H host -p port [-w <warning time>] [-c <critical time>] [-s <send string>] [-e <expect string>] [-q <quit string>][-m <maximum bytes>] [-d <delay>] [-t <timeout seconds>] [-r <refuse state>] [-M <mismatch state>] [-v] [-4|-6] [-j] [-D <warn days cert expire>[,<crit days cert expire>]] [-S <use SSL>] [-E]
check_ldap: This plugin tests LDAP services. It can be tested with a given search.
Usage:
check_ldap -H <host> -b <base_dn> [-p <port>] [-a <attr>] [-D <binddn>]
[-P <password>] [-w <warn_time>] [-c <crit_time>] [-t timeout]
[-2|-3] [-4|-6]
check_ldaps: This plugin tests LDAPS services. It can be tested with a given search.
Usage:
check_ldaps -H <host> -b <base_dn> [-p <port>] [-a <attr>] [-D <binddn>]
[-P <password>] [-w <warn_time>] [-c <crit_time>] [-t timeout]
[-2|-3] [-4|-6]
check_mysql: This plugin tests connections to a MySQL server.
Usage:
check_mysql [-d database] [-H host] [-P port] [-s socket]
[-u user] [-p password] [-S] [-l] [-a cert] [-k key]
[-C ca-cert] [-D ca-dir] [-L ciphers] [-f optfile] [-g group]
check_mysql_query: This plugin checks a query result against threshold levels.
Usage:
check_mysql_query -q SQL_query [-w warn] [-c crit] [-H host] [-P port] [-s socket]
[-d database] [-u user] [-p password] [-f optfile] [-g group]
check_pgsql: Test whether a PostgreSQL Database is accepting connections.
Usage: check_pgsql [-H <host>] [-P <port>] [-c <critical time>] [-w <warning time>] [-t <timeout>] [-d <database>] [-l <logname>] [-p <password>] [-q <query>] [-C <critical query range>] [-W <warning query range>]
check_pop: This plugin tests POP connections with the specified host.
Usage: check_pop -H host -p port [-w <warning time>] [-c <critical time>] [-s <send string>] [-e <expect string>] [-q <quit string>][-m <maximum bytes>] [-d <delay>] [-t <timeout seconds>] [-r <refuse state>] [-M <mismatch state>] [-v] [-4|-6] [-j] [-D <warn days cert expire>[,<crit days cert expire>]] [-S <use SSL>] [-E]
check_radius: Tests to see if a RADIUS server is accepting connections.
Usage: check_radius -H host -F config_file -u username -p password [-P port] [-t timeout] [-r retries] [-e expect] [-n nas-id] [-N nas-ip-addr]
check_simap: This plugin tests secure IMAP connections with the specified host.
Usage: check_simap -H host -p port [-w <warning time>] [-c <critical time>] [-s <send string>] [-e <expect string>] [-q <quit string>][-m <maximum bytes>] [-d <delay>] [-t <timeout seconds>] [-r <refuse state>] [-M <mismatch state>] [-v] [-4|-6] [-j] [-D <warn days cert expire>[,<crit days cert expire>]] [-S <use SSL>] [-E]
check_smtp: This plugin will attempt to open an SMTP connection with the host.
Usage: check_smtp -H host [-p port] [-4|-6] [-e expect] [-C command] [-R response] [-f from addr] [-A authtype -U authuser -P authpass] [-w warn] [-c crit] [-t timeout] [-q] [-F fqdn] [-S] [-D warn days cert expire[,crit days cert expire]] [-v]
check_snmp: Check the status of remote machines and obtain system information via SNMP.
Usage: check_snmp -H <ip_address> -o <OID> [-w warn_range] [-c crit_range] [-C community] [-s string] [-r regex] [-R regexi] [-t timeout] [-e retries] [-l label] [-u units] [-p port-number] [-d delimiter] [-D output-delimiter] [-m miblist] [-P snmp version] [-N context] [-L seclevel] [-U secname] [-a authproto] [-A authpasswd] [-x privproto] [-X privpasswd] [-4|6]
check_spop: This plugin tests secure POP connections with the specified host.
Usage: check_spop -H host -p port [-w <warning time>] [-c <critical time>] [-s <send string>] [-e <expect string>] [-q <quit string>][-m <maximum bytes>] [-d <delay>] [-t <timeout seconds>] [-r <refuse state>] [-M <mismatch state>] [-v] [-4|-6] [-j] [-D <warn days cert expire>[,<crit days cert expire>]] [-S <use SSL>] [-E]
check_ssh: Try to connect to an SSH server at specified server and port.
Usage: check_ssh [-4|-6] [-t <timeout>] [-r <remote version>] [-p <port>] <host>
check_ssmtp: This plugin tests SSMTP connections with the specified host.
Usage: check_ssmtp -H host -p port [-w <warning time>] [-c <critical time>] [-s <send string>] [-e <expect string>] [-q <quit string>][-m <maximum bytes>] [-d <delay>] [-t <timeout seconds>] [-r <refuse state>] [-M <mismatch state>] [-v] [-4|-6] [-j] [-D <warn days cert expire>[,<crit days cert expire>]] [-S <use SSL>] [-E]
check_tcp: This plugin tests TCP connections with the specified host.
Usage: check_tcp -H host -p port [-w <warning time>] [-c <critical time>] [-s <send string>] [-e <expect string>] [-q <quit string>][-m <maximum bytes>] [-d <delay>] [-t <timeout seconds>] [-r <refuse state>] [-M <mismatch state>] [-v] [-4|-6] [-j] [-D <warn days cert expire>[,<crit days cert expire>]] [-S <use SSL>] [-E]
For further information, execute the following command under the plugins path:
plugin_name --help
Farm Guardian will use these plugins to check the health status of the backends and will manage the execution error output of the executed plugin in order to decide the backend status as follows:
If the error output == 0 then the backend is OK > $? = 0
If the error output <> 0 then the backend is NOT OK > $? <> 0
Custom plugin
These plugins can be configured and fully programmable by sysadmins in order to be adapted to any protocol or application.
This example shows a custom plugin check_load.sh.
#!/bin/bash ### ###comments: ###snmp utils should be installed ###snmpd should be installed and configured in the backends ### MAXVALUE=4 COMMUNITY="public" EXECUTE=`snmpget -v 2c -c $COMMUNITY $1 .1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.3.1 |cut -d ':' -f2 | cut -d '.' -f1 | sed s/\ // | sed s/\"//` echo "SNMP CPU load check for $1 is $EXECUTE" # If the result is true, exit with 1; error; else exit = 0; OK if (( $EXECUTE >= $MAXVALUE )); then #error output; the server is overloaded and the load balancer isn’t going to send more connections exit 1 else #not error; the server can accept more connections exit 0 fi
Constants
When Farmguardian executes a plugin, it can use some constants or tokens as arguments, like:
- HOST: Farmguardian will take care of modifying this constant by the real server IP address.
- PORT: Farmguardian will take care of modifying this constant by the real server port.
These constants can be used for every plugin, Farmguardian will use them to run the health check with the real parameters in place.
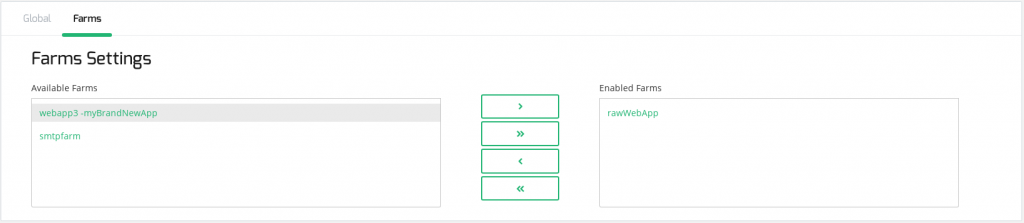
Farms
On this tab, there is a list of farms and services using this Farmguardian health check.
Farms and services can be assigned or removed from this Farmguardian health check using multiple selections with single arrow icons or double arrows to enable or disable all farms.