Contents
This section shows all the settings available for the current blacklist organized in two tabs Global and Farms. Keep in mind that every change in this section has to be applied clicking on the Update button.
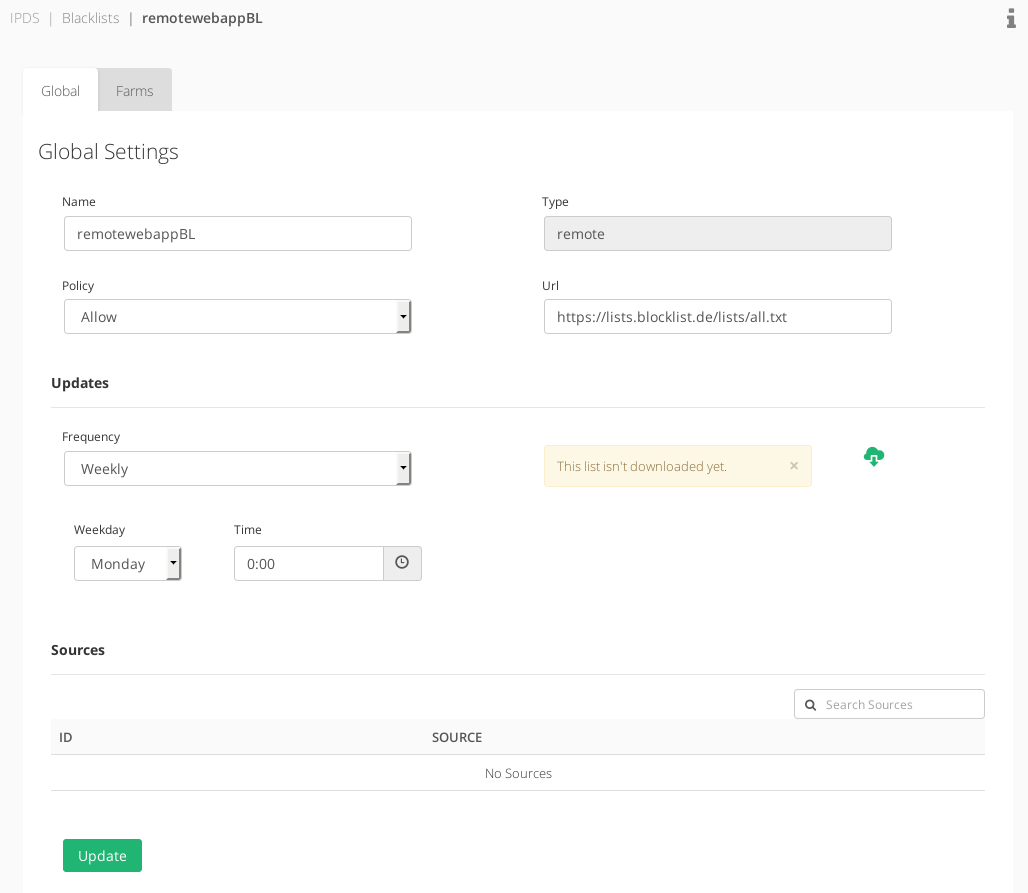
The Global Settings for Local or Remote blacklists includes the creation required fields Name, Type and Policy.
If the blacklist is preloaded it’s not possible to modify it, only user created ones can be modified.
Global Settings Local Blacklists
The Local Blacklists require to add the list of IP addresses or subnets as a list in the Sources section.
Name: should be self-explained in order to be easily found and recognizable
Type: In this case we are configuring a local Rule, what means that you manually will introduce a list of custom IP
Policy: Can be one of the following, Allow or Deny, dependig of the effect you would like to aply to your custon IP list.
Source
The Sources section includes the following information:
ID. It’s the index that references the source in the blacklist.
SOURCE. The source IP address or source subnet in IPv4 format.
ACTION. The available actions per source are:
- Add Source. Add a new IP or net source into the blacklist.
- Save. Save the new entry in the given blacklist and start using it.
- Cancel. Cancel the new entry in the blacklist.
- Delete. Delete the given IP or net source from the blacklist.
- Edit. Modify a certain IP source or subnet from the blacklist.
Those action are only possible when the list is a customized list by the user and it is local Type of list. It does not work on remote lists or preloaded lists. The action can be accomplished by clicking over the source.
Global Settings Remote Blacklists
The global settings that a Remote Blacklist includes are described below.
Updates
The Updates section permits to schedule the download and update of the remote blacklist:
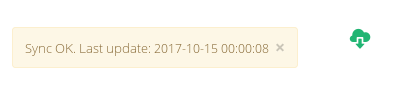
There is a Green cloudy button for you to download the blacklist you set in the Url field.
This way you can check if the url link works as expected without waiting the scheduled set in the following section.
Frequency. Update frequency of the blacklist. The options available are:
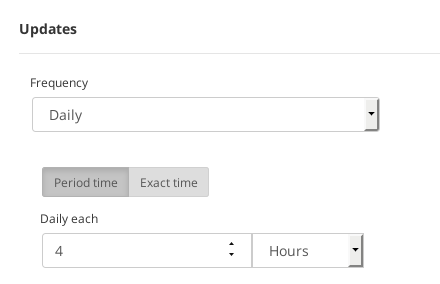
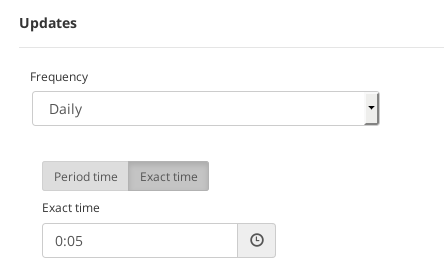
- Daily. The blacklist will be updated in a daily basis. It’s available to select a Period time in order to update it several times per day or an Exact time in order to update it once a day at a certain time.


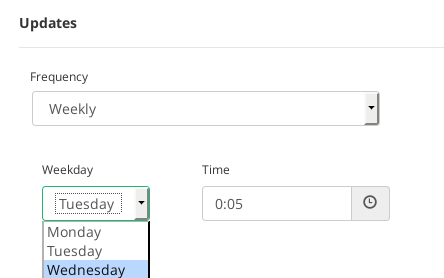
- Weekly. The blacklist will be updated in a weekly basis. It’s needed to select a Weekday when the update will be executed once a week at a certain Time.

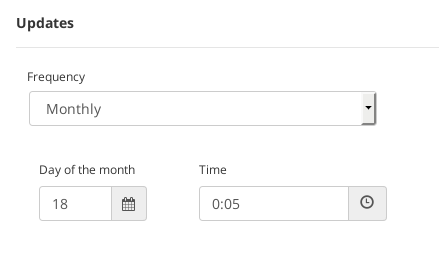
- Monthly. The blacklist will be updated in a monthly basis. It’s needed to select the Day of the month when the update will be executed once every month at a certain Time.

The format of the remote file should be a text/plain file with a line per IP address or subnet to add into the blacklist.
Here you can see an example of a correct blacklist format:
Notice that each line is formed by only an IPv4 address.
If you would like to include an entire Subnet Range you should use this format to represent the mask: ipv4_address/bits
For example: 172.14.43.0/24 will affect IP address from 172.14.43.1 to 172.14.43.254
Farms Blacklists Settings
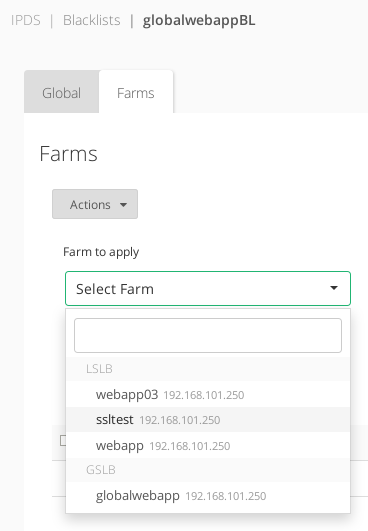
This section allows to assign farms to the preloaded or created blacklists, through the Farms tab when updating a blacklist.
The available actions in this section are:
- Add Farm. Add a new farm service in a given blacklist. When assigning a new farm, a combo list of all the configured farms will be shown, either they’re running or not.

- Unset. Deallocate a farm service to a certain blacklist and stop applying the blacklist policy to a given farm service.
The actions are applied one by one, or by a group of farms services through the multiple selector.